What Causes Urticaria and How Can You Prevent It?
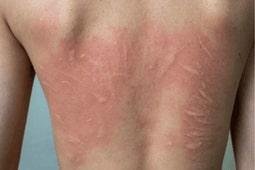
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by raised, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the body. These welts, often red or skin-colored, may vary in size and shape and can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (persisting beyond six weeks). Understanding the causes of urticaria and implementing preventive measures is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
What is Urticaria?
Urticaria occurs when the skin releases histamine and other chemicals into the bloodstream, causing small blood vessels to leak fluid into the skin, resulting in welts or wheals. These welts are often accompanied by itching, burning, or stinging sensations. In some cases, urticaria may be associated with angioedema, a deeper swelling of the skin that affects areas like the lips, eyes, or throat. The condition can be triggered by various factors, ranging from allergens to underlying medical conditions.
Causes of Urticaria
Urticaria can be triggered by a wide range of factors, and identifying the specific cause is often key to effective management. Below are the primary causes of urticaria:
1. Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions are a common cause of acute urticaria. These reactions occur when the immune system overreacts to a substance, leading to histamine release. Common allergens include:
-
Foods: Peanuts, shellfish, eggs, milk, and wheat are frequent culprits.
-
Medications: Antibiotics (including cephalexin capsules in rare cases), aspirin, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can trigger hives in sensitive individuals.
-
Insect Bites or Stings: Bee or wasp stings may cause localized or widespread hives.
-
Environmental Allergens: Pollen, pet dander, or dust mites can provoke an allergic response.
2. Infections
Infections, particularly viral ones, are a significant cause of urticaria, especially in children. Bacterial infections, such as those caused by Streptococcus or Helicobacter pylori, can also trigger hives. In some cases, cephalexin capsules, a commonly prescribed antibiotic from a reputable cephalexin capsules supplier, may be used to treat bacterial infections that contribute to urticaria. However, it’s worth noting that antibiotics themselves can occasionally cause hives as a side effect in allergic individuals.
3. Physical Triggers
Physical urticaria is caused by direct physical stimulation of the skin. Common physical triggers include:
-
Pressure: Tight clothing or prolonged pressure on the skin can cause dermatographism, a form of urticaria where welts form after scratching.
-
Temperature: Exposure to extreme heat, cold, or sunlight can induce hives in susceptible individuals.
-
Exercise or Sweating: Physical activity or sweating can trigger cholinergic urticaria, characterized by small, itchy welts.
4. Autoimmune Disorders
Chronic urticaria is often linked to autoimmune conditions, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. Conditions like lupus, thyroid disease, or rheumatoid arthritis may be associated with chronic hives. In such cases, managing the underlying autoimmune condition is essential to reducing urticaria symptoms.
5. Stress
Emotional or psychological stress can exacerbate or trigger urticaria in some individuals. Stress-induced hives may occur due to the release of stress hormones that stimulate histamine production.
6. Medications and Supplements
Certain medications, including cephalexin capsules, can cause urticaria as a side effect, particularly in those with a predisposition to drug allergies. Always source medications from a trusted cephalexin capsules supplier to ensure quality and minimize risks. Other drugs, such as ACE inhibitors or opioids, may also provoke hives.
7. Underlying Medical Conditions
Chronic urticaria may be a symptom of underlying medical conditions, such as thyroid dysfunction, liver disease, or kidney issues. In rare cases, urticaria can be a sign of malignancy, requiring thorough medical evaluation.
Symptoms of Urticaria
The hallmark symptom of urticaria is the appearance of raised, red, or skin-colored welts that are typically itchy. These welts may:
-
Vary in size from small dots to large patches.
-
Appear and disappear within hours, often moving to different areas of the body.
-
Be accompanied by swelling (angioedema) in severe cases.
-
Cause discomfort or a burning sensation.
In cases of severe allergic reactions, urticaria may be accompanied by symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, or dizziness, which require immediate medical attention.
How to Prevent Urticaria
Preventing urticaria involves identifying and avoiding triggers, managing underlying conditions, and adopting lifestyle changes to reduce the likelihood of flare-ups. Below are practical strategies to prevent urticaria:
1. Identify and Avoid Triggers
-
Keep a Symptom Diary: Track when hives appear, noting potential triggers like foods, medications, or environmental factors. This can help pinpoint specific causes.
-
Allergy Testing: Consult an allergist to identify specific allergens through skin or blood tests. Avoiding known allergens, such as certain foods or pet dander, can prevent allergic urticaria.
-
Check Medications: If you suspect a medication like cephalexin capsules is causing hives, consult your healthcare provider. Ensure medications are sourced from a reliable cephalexin capsules supplier to avoid counterfeit products that may increase risks.
2. Manage Infections Promptly
Since infections can trigger urticaria, prompt treatment is essential. For bacterial infections, antibiotics like cephalexin capsules from a trusted cephalexin capsules supplier may be prescribed. Always complete the full course of antibiotics as directed to prevent recurrence of infections that could lead to hives.
3. Minimize Physical Triggers
-
Dress Comfortably: Wear loose-fitting clothing to avoid pressure-induced hives.
-
Protect Against Temperature Extremes: Use sunscreen, wear protective clothing in the sun, or bundle up in cold weather to prevent temperature-related urticaria.
-
Cool Down After Exercise: If exercise triggers hives, take cool showers and avoid overheating.
4. Manage Stress
Stress management techniques can reduce the likelihood of stress-induced hives. Practices like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or regular exercise can help lower stress levels. Seeking professional support, such as therapy, may also be beneficial for chronic stress.
5. Follow a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet can support overall immune health and reduce the risk of allergic reactions. Avoid known food triggers and incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3-rich fish. If food allergies are suspected, work with a dietitian to create an elimination diet plan.
6. Use Medications Wisely
For individuals with chronic urticaria, antihistamines are often the first line of treatment to reduce histamine release and alleviate symptoms. In cases where bacterial infections are a trigger, cephalexin capsules from a reputable cephalexin capsules supplier may be prescribed to address the underlying infection. Always follow your doctor’s guidance and report any adverse reactions to medications promptly.
7. Regular Medical Check-Ups
If you have chronic urticaria, regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor underlying conditions like thyroid disease or autoimmune disorders. Blood tests or other diagnostics may be needed to identify and manage these conditions effectively.
8. Emergency Preparedness
For those prone to severe allergic reactions, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (e.g., EpiPen) is critical. Learn how to use it and ensure family members or close contacts are aware of its location and purpose.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While mild cases of urticaria can often be managed at home, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
-
Difficulty breathing or swallowing.
-
Swelling of the face, lips, or throat.
-
Dizziness or fainting.
-
Persistent hives lasting more than six weeks despite treatment.
In such cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe medications like cephalexin capsules for infection-related urticaria or other treatments to address severe allergic reactions.
Conclusion
Urticaria is a complex condition with diverse causes, ranging from allergies and infections to physical triggers and stress. By identifying triggers, managing underlying conditions, and adopting preventive strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of hives. For those with infection-related urticaria, medications like cephalexin capsules from a trusted cephalexin capsules supplier can be part of an effective treatment plan when prescribed by a healthcare provider. Always consult a medical professional for personalized advice and treatment options to manage urticaria effectively.






