-
Feed de Notícias
- EXPLORAR
-
Blogs
-
Grupos
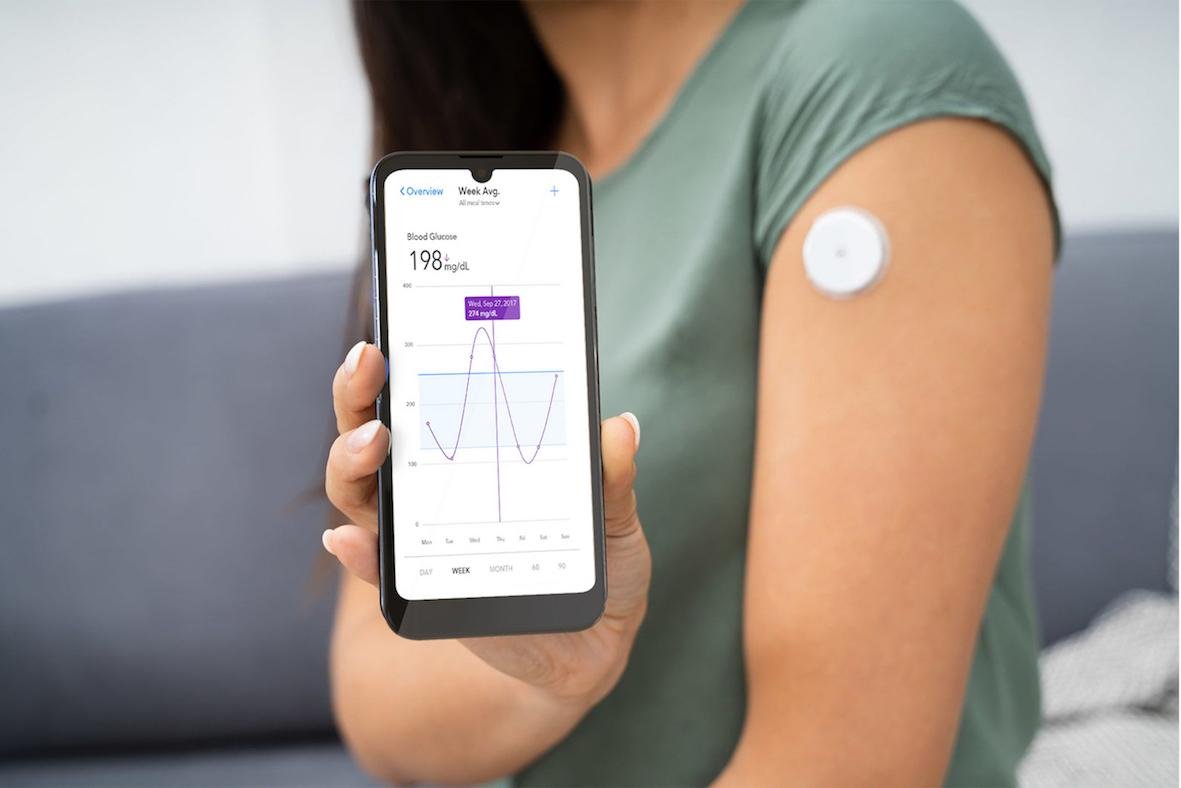
Glucose Sensors Market: Journey Toward Minimally Invasive and User-Friendly Devices
Introduction
As the global burden of diabetes rises, the Glucose Sensors Market continues to innovate to meet evolving patient needs. A major trend gaining momentum is the transition toward minimally invasive and user-friendly glucose monitoring devices. This shift aims to reduce discomfort, improve compliance, and empower individuals to manage their blood sugar levels more independently and efficiently.
This article explores how the market is progressing toward gentler, more convenient glucose sensing technologies, and how this transformation is redefining diabetes care for millions of users worldwide.
Why Minimally Invasive Solutions Matter
Traditional finger-prick tests and even some Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) devices require frequent calibration or cause discomfort due to insertion methods. This has led to:
-
User fatigue and non-compliance
-
Reduced monitoring frequency
-
Delayed interventions
-
Higher healthcare risks
To address these issues, manufacturers are investing heavily in sensor miniaturization, painless application systems, and extended wearability, all while maintaining clinical accuracy.
Key Technological Advances Toward Minimal Invasiveness
1. Microneedle-Based Sensors
Microneedle patches penetrate only the upper skin layer, causing minimal or no pain. These sensors can:
-
Continuously extract interstitial fluid for glucose readings
-
Be self-applied and worn discreetly
-
Reduce the risk of infection or irritation
Startups and research institutions are accelerating development in this area with promising prototypes and pilot studies.
2. Optical and Transdermal Sensors
These technologies use light, heat, or ultrasonic waves to detect glucose levels beneath the skin without breaking it. Though still developing, companies are:
-
Improving accuracy using advanced AI signal processing
-
Working to overcome issues like skin tone variability and ambient interference
-
Creating smartphone-integrated devices for seamless usability
3. Long-Lasting Implantable Sensors
Example: Senseonics' Eversense XL
-
Inserted under the skin by a healthcare provider
-
Can function for up to 180 days
-
Transmits data wirelessly to mobile apps
-
Offers a solution for users tired of regular sensor replacements
This category represents a bridge between invasive and fully non-invasive monitoring.
User-Centric Design: The New Frontier
Minimally invasive tech is only one part of the puzzle. User-friendly design is equally vital for adoption and long-term success. Companies are focusing on:
-
Slimmer and smaller devices for discretion
-
Waterproof wearables for continuous lifestyle integration
-
Smartphone compatibility for real-time feedback and logging
-
Auto-applicators to simplify placement and reduce user error
-
Haptic and audio alerts to help visually impaired users
Design now prioritizes the user’s daily experience, moving beyond clinical functionality to true lifestyle integration.
Major Players Leading the Shift
| Company | Minimally Invasive Feature |
|---|---|
| Dexcom | Dexcom G7 – no fingersticks, compact, wearable, 10-day use |
| Abbott | FreeStyle Libre 3 – small profile, pain-free applicator |
| Senseonics | Eversense – implantable for up to 180 days |
| PKvitality | K’Watch Glucose – smart watch with skin sensor (in development) |
| Know Labs | Non-invasive RF spectroscopy technology |
These companies are reimagining what it means to monitor glucose, making it less about medicine and more about smart living.
Benefits to Users and Healthcare Systems
-
Improved Patient Compliance: Comfortable and low-maintenance sensors encourage regular monitoring.
-
Enhanced Quality of Life: Reduced pain and fewer disruptions to daily activities.
-
Early Detection and Intervention: Consistent use leads to better glycemic control.
-
Lower Healthcare Costs: Fewer complications and hospital visits due to better self-management.
In essence, the more convenient the technology, the more empowered the patient.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While the progress is notable, challenges remain:
-
Balancing accuracy and comfort in non-invasive models
-
Ensuring sensor longevity without compromising performance
-
Gaining regulatory approvals for new technologies
-
Reducing costs for wider adoption in low- and middle-income countries
However, the future holds immense promise. Advancements in biomaterials, nanotechnology, and AI will soon make even the most ambitious designs a reality.
Conclusion
The Glucose Sensors Market is undergoing a transformative journey—from bulky, painful systems to sleek, user-friendly wearables and implantables. With a clear focus on minimally invasive solutions and intuitive usability, the market is empowering users with freedom, comfort, and better health outcomes. As the boundary between medical device and lifestyle wearable continues to blur, glucose monitoring is poised to become not just easier—but invisible, seamless, and personalized.






