-
Feed de notícias
- EXPLORAR
-
Blogs
Understanding Pubertal Gynecomastia and Its Timeline
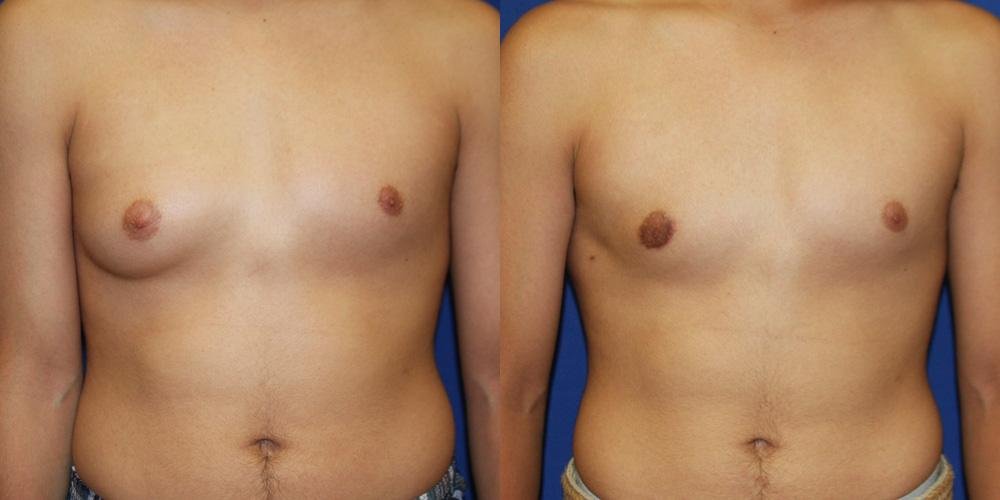
Pubertal gynecomastia refers to the temporary enlargement of breast tissue in adolescent boys. This condition is typically linked to hormonal changes during puberty. It occurs when the balance between estrogen and testosterone shifts, leading to a slight increase in breast tissue. While it may cause concern for young boys and their families, pubertal Gynecomastia Dubai is generally a normal part of development and tends to resolve on its own over time.
Why Does It Happen?
During puberty, the body undergoes a surge in hormones that trigger growth and physical changes. Testosterone levels rise, but small amounts of estrogen are also present. Sometimes estrogen levels are relatively higher compared to testosterone, which can cause the breast tissue to enlarge temporarily. This hormonal fluctuation is usually short-term and part of the natural growth process.
Common Signs and Symptoms
The most noticeable symptom of pubertal gynecomastia is the appearance of firm or rubbery tissue under the nipple area. Some boys may notice slight tenderness or sensitivity, while others experience no discomfort at all. Typically, the enlargement affects one or both breasts, though it can be asymmetrical.
Typical Age of Onset
Pubertal gynecomastia commonly begins between the ages of 12 and 16. This timing coincides with the rapid hormonal shifts that occur during early adolescence. The condition can appear suddenly or develop gradually over several months, depending on individual hormonal changes.
Timeline of Pubertal Gynecomastia
The timeline of pubertal gynecomastia varies for each individual, but a general pattern can be observed. Early stages often involve minor swelling and slight tenderness. Over the following months, the tissue may increase in size before gradually stabilizing. Most cases reach a peak within six to twelve months, after which the breast tissue slowly regresses. Complete resolution typically occurs within one to three years after onset, though some cases may take slightly longer.
Duration and Resolution
For the majority of adolescent boys, pubertal gynecomastia resolves naturally without intervention. As hormone levels stabilize, the excess breast tissue diminishes and the chest returns to a more typical appearance. While the process may feel slow, it is important to remember that it is part of normal development and usually does not require treatment.
Psychological Impact
The appearance of breast tissue can be distressing for teenagers, affecting self-esteem and confidence. Social situations such as changing clothes for sports or participating in physical activities may cause discomfort or embarrassment. Open communication and reassurance from family and peers can help mitigate anxiety. Understanding that this condition is common and temporary often provides significant relief.
Factors That Influence Development
Several factors can affect the severity and duration of pubertal gynecomastia. Hormonal balance is the primary determinant, but genetics, body weight, and overall growth patterns may also play a role. Boys with higher body fat percentages may notice more pronounced breast tissue due to fat accumulation in addition to glandular growth.
When to Monitor
Although pubertal gynecomastia is typically benign, it is important to monitor changes in breast tissue. Rapid growth, significant asymmetry, or persistent enlargement beyond the usual timeline may require attention. Observing the progression allows families and caregivers to distinguish between normal development and conditions that might need further evaluation.
Coping Strategies for Adolescents
Adolescents can benefit from strategies that help them manage the emotional and social effects of pubertal gynecomastia. Wearing loose-fitting clothing or layering shirts can reduce self-consciousness. Focusing on activities that boost confidence and body image, such as sports or hobbies, can also be helpful. Peer support and reassurance that the condition is temporary play an essential role in coping.
FAQs
How long does pubertal gynecomastia usually last?
Most cases resolve within one to three years, with the peak enlargement occurring around six to twelve months after onset.
Is it normal for only one breast to be affected?
Yes, it is common for gynecomastia to be asymmetrical. One breast may appear slightly larger than the other, and this is typically part of normal development.
Does pubertal gynecomastia cause pain?
Some boys experience mild tenderness or sensitivity, but severe pain is uncommon. Discomfort usually decreases as the tissue gradually regresses.
Can gynecomastia return after it resolves?
It is uncommon for pubertal gynecomastia to recur once hormonal levels stabilize. Occasional changes during later adolescence may occur but typically do not lead to significant tissue growth.
Should adolescents worry about gynecomastia affecting puberty?
Pubertal Gynecomastia in Dubai does not interfere with normal growth or development. It is a temporary condition that generally resolves on its own without affecting overall puberty.
Understanding pubertal gynecomastia and its timeline helps families and adolescents approach this common condition with reassurance and perspective. Recognizing that hormonal fluctuations are natural and temporary can reduce anxiety and support healthy self-image during adolescence.




